'Magnificent Highland Rim: A Geological Wonder' provides a comprehensive exploration of the geological marvels and natural resources present in the Highland Rim region.
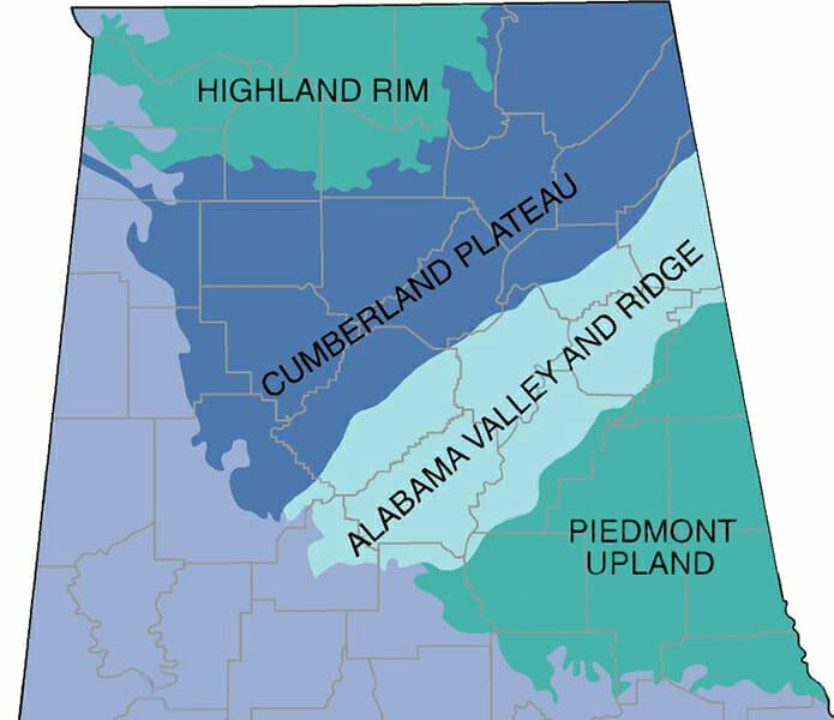
Situated in the Southernmost section of the Interior Low Plateaus province in the Appalachian Highlands Region, this area encompasses approximately 7 percent of Alabama, extending into Tennessee and Kentucky.
The article delves into the distinct geological features, such as the differential erosion of middle- to upper-Paleozoic sedimentary rocks and the three unique districts within the Highland Rim.
Furthermore, it examines the significance of the Tennessee River and the economic importance of limestone extraction from quarries in the area.
With a focus on the region's captivating landscape and geological significance, the article offers valuable insights for those seeking mastery in geological studies.
Key Takeaways
- The Highland Rim is located in the southernmost section of the Interior Low Plateaus province in the Appalachian Highlands Region, spanning northwest and north central Alabama, Tennessee, and Kentucky.
- The Highland Rim is characterized by valleys, ridges, and cliffs, with the Tennessee Valley district occupying most of the region.
- The main ridge-forming rock in the Highland Rim is the Hartselle Sandstone, while the valleys are cut through the Bangor Limestone and Tuscumbia Limestone Formations.
- The Tennessee River flows through the Highland Rim, with its tributaries originating from Little Mountain and the northern uplands. The construction of Wilson and Wheeler Dams made the river navigable, and the Tennessee Valley Authority operates three hydroelectric plants on the river.
Geological Formation
The geological formation of the Highland Rim is primarily characterized by the differential erosion of middle- to upper-Paleozoic sedimentary rocks, resulting in the creation of its distinct landforms. These landforms are a testament to the intricate geological processes that have shaped the region over millions of years.
The Hartselle Sandstone, a prominent ridge-forming rock, and the Bangor Limestone and Tuscumbia Limestone Formations have played a pivotal role in shaping the rock formations and land features of the Highland Rim.
The Mississippian period, dating back 353 to 323 million years before the present, marks a significant era in the geological history of this area.
The ongoing geological processes continue to influence the rock formations and landforms, making the Highland Rim a captivating subject for those seeking to comprehend the complexities of geological evolution.
Districts and Landforms
A thorough understanding of the geological formation of the Highland Rim naturally leads to an exploration of its distinct districts and the remarkable landforms that define them.
Comprising the Tennessee Valley, Little Mountain, and Moulton Valley, the Highland Rim is characterized by valleys, ridges, and cliffs that shape its landscape. Valley formations, such as those cut through the Bangor Limestone and Tuscumbia Limestone Formations, contribute to the unique topography of the region.
The district of Little Mountain forms the northern border of Moulton Valley, which separates the Warrior Basin from Little Mountain. These ridge characteristics and valley formations not only add to the geological wonder of the Highland Rim but also play a significant role in shaping the natural resources and economic activities of the area.
Tennessee River
Flowing through the Highland Rim in a northwesterly direction, the Tennessee River is a significant geographical feature in the region. The river, along with its tributaries, forms a complex and dynamic river ecosystem.
Historically characterized by rapids, shoals, and shallow water, the construction of Wilson and Wheeler Dams has made the Tennessee River navigable. The Tennessee Valley Authority operates three hydroelectric plants on the river, harnessing its power for energy production.
The river also serves as a vital resource for the extraction of limestone from the Tuscumbia and Bangor Formations, which is used as construction aggregate and for architectural and decorative purposes.
The Tennessee River, with its rich history and ecological significance, plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape and economy of the Highland Rim.
Hydroelectric Power
Positioned strategically along the Tennessee River, hydroelectric power plays a significant role in shaping the economy and energy production of the Highland Rim.
- Renewable Energy: Hydroelectric power harnesses the natural flow of water to generate electricity, providing a sustainable and renewable energy source for the region.
- Environmental Impact: The construction of hydroelectric dams has both positive and negative environmental impacts, including alterations to river flow, impacts on aquatic ecosystems, and potential changes in water quality.
- Economic Influence: The presence of hydroelectric power plants contributes to the economic development of the Highland Rim, providing jobs and supporting local industries.
- Sustainability: By utilizing the water resources of the Tennessee River, hydroelectric power contributes to the region's overall sustainability efforts, reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Limestone Quarries
The extraction of limestone from quarries plays a pivotal role in the economic and industrial landscape of the Highland Rim, contributing significantly to the region's development and prosperity. Limestone quarries primarily extract from Tuscumbia and Bangor Formations, providing construction aggregate and dimension stone for architectural and decorative purposes. However, this activity has raised concerns about its environmental impact, prompting conservation efforts to mitigate potential harm. Efforts to minimize the impact of limestone quarrying include reclamation of quarried areas, restoration of natural habitats, and implementation of sustainable mining practices. By prioritizing environmental conservation alongside extraction, the Highland Rim can ensure the responsible utilization of its natural resources.
| Environmental Impact | Conservation Efforts |
|---|---|
| Habitat disruption | Reclamation of quarried areas |
| Water pollution | Restoration of natural habitats |
| Air pollution | Sustainable mining practices |
Natural Resource Extraction
Natural resource extraction in the Highland Rim plays a crucial role in the region's economic development and industrial activity.
- The limestone industry is a significant contributor to the region's economy, providing construction aggregate and dimension stone for architectural and decorative purposes.
- Quarrying operations primarily target the Tuscumbia and Bangor Formations, which are rich in limestone deposits.
- The extraction of natural resources, especially limestone, underscores the economic importance of the Highland Rim, supporting various construction and infrastructure projects.
- Resource conservation efforts are essential to ensure sustainable extraction practices and the long-term viability of the limestone industry in the region.
The responsible management of natural resources, particularly within the limestone industry, is crucial for balancing economic growth with environmental preservation in the Highland Rim.
Environmental Significance
With a focus on environmental significance in the Highland Rim, responsible management of natural resources, particularly within the limestone industry, is crucial for balancing economic growth with environmental preservation.
The impact on biodiversity from limestone quarrying and extraction necessitates stringent conservation efforts to safeguard the region's unique flora and fauna. Conservation programs should prioritize the protection of endemic species and the restoration of habitats affected by quarrying activities.
Implementing sustainable practices, such as reclamation of quarried areas and the establishment of protected zones, is vital to mitigate the environmental impact of resource extraction.
Furthermore, fostering partnerships between industry stakeholders, environmental organizations, and governmental bodies can facilitate the development and enforcement of comprehensive conservation strategies to ensure the long-term ecological health of the Highland Rim.
Economic Impact
Economic impact is a significant consideration in the management of the Highland Rim's natural resources, particularly in the limestone industry. The limestone industry has a profound effect on the region's economy, primarily through job creation. Here are some key points highlighting its economic impact:
- Job Creation: Limestone quarries in the Highland Rim provide employment opportunities for the local population, contributing to economic growth and stability.
- Industrial Development: The extraction and processing of limestone support the development of various industries, such as construction, architecture, and infrastructure.
- Economic Growth: The abundance of natural limestone resources in the region fuels economic growth, attracting investments and fostering business activities.
- Regional Prosperity: The limestone industry plays a crucial role in sustaining the economic prosperity of the Highland Rim, enhancing its overall socio-economic landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Potential Environmental Impacts of Limestone Quarrying in the Highland Rim?
Limestone quarrying in the Highland Rim may lead to water pollution and habitat destruction due to runoff and disturbance of ecosystems. Air quality can be affected by dust and particulate matter, while landscape alteration may impact visual aesthetics.
How Has the Tennessee River's Ecosystem Been Affected by the Construction of Hydroelectric Dams?
The construction of hydroelectric dams on the Tennessee River has significantly altered its ecosystem. Changes include altered flow patterns, impacts on fish migration, and the creation of reservoirs, affecting water quality and habitats for aquatic life.
What Are the Economic Benefits and Drawbacks of Natural Resource Extraction in the Highland Rim?
Economic benefits of natural resource extraction in the Highland Rim include revenue generation and job creation. However, environmental drawbacks such as habitat disruption and water pollution must be carefully managed to ensure sustainable development and preservation of the region's natural beauty.
Are There Any Endangered Species or Unique Habitats Within the Highland Rim That Are of Ecological Significance?
The Highland Rim harbors endangered species and unique habitats of ecological significance, contributing to biodiversity conservation. The region's diverse geology sustains a variety of ecosystems, highlighting the need for comprehensive habitat preservation and protection measures.
How Has the Geological Formation of the Highland Rim Influenced the Region's Cultural and Historical Development?
The geological formation of the Highland Rim has significantly shaped the region's cultural and historical development. Its rugged terrain, limestone resources, and the Tennessee River have influenced settlement patterns, economic activities, and the development of local traditions and heritage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Highland Rim stands as a geological masterpiece, with its towering landforms and rich natural resources. Like a grand canvas painted by nature, the region's distinct districts and the flow of the Tennessee River create a breathtaking sight.
The extraction of limestone from quarries and the harnessing of hydroelectric power from the river further add to the region's economic and environmental significance.
The Highland Rim truly embodies the beauty and power of the earth's geological wonders.
Our Reader’s Queries
What physiographic region is the Highland Rim in?
The Highland Rim, the southernmost portion of a chain of low plateaus within the Appalachian Mountains, is one of Alabama’s five physiographic regions. It is the smallest region in the state, covering approximately 7 percent of the land.
What is special about Highland Rim Alabama?
Apart from some wide stream bottoms, the land is mostly made up of ridges and valleys with a couple of low hills. The area is filled with plenty of perennial streams, ensuring ample water supply. Every now and then, there are waterfalls that serve as markers, distinguishing the Highland Rim from the encompassing Central Basin.
What cities are in the Highland Rim Alabama?
Dams have flooded many of the big lowland areas. The region is fairly populated, especially in the south, with Huntsville, AL being the biggest city, and Decatur, AL, Florence, AL, and Cookeville, TN following closely behind. There is a lot of suburban growth around these cities.
What physiographic region is Alabama in?
Sapp and Emplaincourt identified five physiographic sections in Alabama, with three in the Appalachian Highlands Region and one each in the Inland Plains and the Atlantic Plain Regions.
Check Out For More References