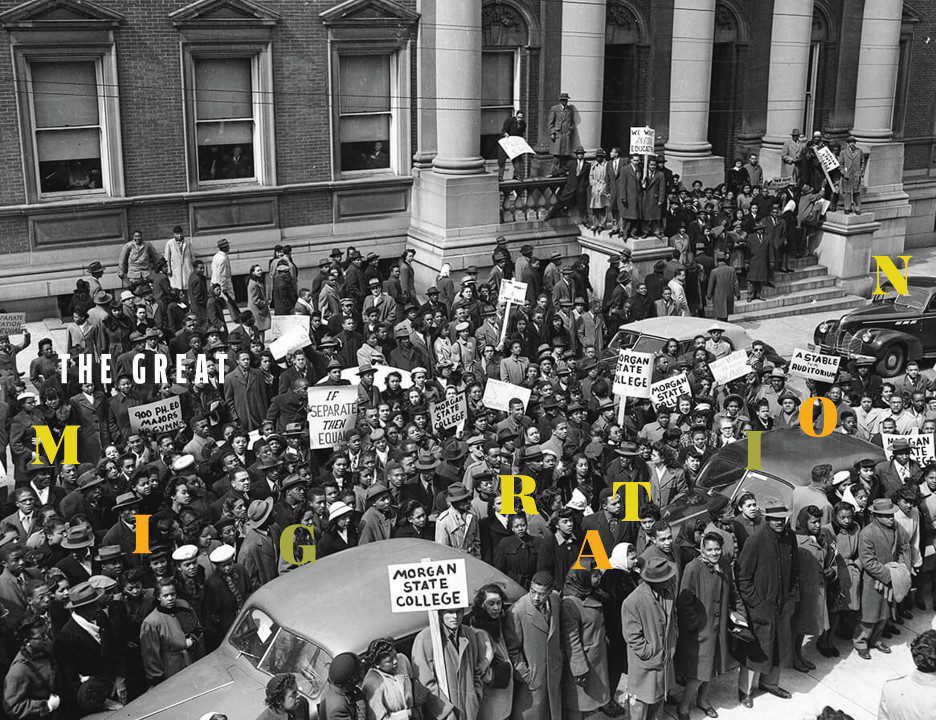'Mass Exodus: Alabama's Impact on Great Migration' delves into the pivotal historical event of the Great Migration, with a specific emphasis on the influential role of Alabama in this transformative movement.
This article meticulously explores the multifaceted catalysts driving the mass exodus of African Americans from the South, including the economic, social, and political factors that propelled this migration.
It meticulously examines the impact of this migration on both African American and American society, from the emergence of influential leaders and community institutions to its profound influence on cultural and artistic expression.
By scrutinizing the causes, effects, and influential figures of the Great Migration, this article provides a comprehensive understanding of the historical significance of Alabama's role in this epochal event.
Key Takeaways
- Economic and political oppression in the South contributed to the Great Migration from Alabama.
- The lure of industrial jobs, better education, and homeownership in the North and West attracted African Americans.
- Influential African American leaders and organizations, such as W. E. B. DuBois and the NAACP, played a significant role during the Great Migration.
- The Great Migration had a profound impact on African Americans, leading to the formation of community institutions, political activism, artistic expression, and contributions to the New Negro Renaissance.
Causes of the Great Migration
Due to economic and political oppression in the South, as well as legal segregation and discrimination in Alabama, the Great Migration was driven by a complex interplay of factors.
Economic and political oppression created a hostile environment for African Americans, compelling them to seek better opportunities elsewhere.
Additionally, ecological disasters and labor shortages further exacerbated the already dire situation, leaving many African American families struggling to make ends meet.
The scarcity of work opportunities due to labor shortages led to increased poverty and limited prospects for a better life.
These circumstances, combined with the hope for a more equitable and just society, prompted the mass movement of African Americans from the South to the North and West.
The Great Migration was a response to the convergence of these compelling factors, marking a pivotal moment in the history of the United States.
Factors Attracting African Americans
The Great Migration was driven not only by the push factors of economic and political oppression in the South, but also by the pull factors that attracted African Americans to the North and West. These factors included:
- Racial tolerance and personal freedom in metropolitan centers
- A chance to escape the systemic racism and discrimination prevalent in the South, offering hope and new opportunities for a better life.
- The promise of a society where individuals are judged by their merits, not the color of their skin.
Access to better education
- The opportunity for African American children to receive a quality education, equipping them with the tools to pursue their dreams and aspirations.
- The potential to break the cycle of poverty and inequality through knowledge and learning.
These pull factors provided African Americans with opportunities for change and access to education, laying the foundation for a brighter future.
Influential African American Leaders
Several influential African American leaders played pivotal roles in the Great Migration, shaping the movement and its outcomes. Notably, W. E. B. DuBois, Marcus Garvey, and Mary McLeod Bethune provided inspiration and guidance to those seeking better opportunities in the North and West. Oscar De Priest and Arthur W. Mitchell also stood as role models, demonstrating the potential for success in political arenas. Additionally, black newspapers such as the Chicago Defender and Pittsburgh Courier played a crucial role in disseminating information and advocating for the rights and opportunities of African Americans. These leaders and organizations provided essential support, guidance, and representation for those seeking to escape the oppressive conditions in the South. Their influence was instrumental in empowering and mobilizing African American communities during the Great Migration.
The table representation is as follows:
| Influential Leaders | Role |
|---|---|
| W. E. B. DuBois | Inspiration and Guidance |
| Marcus Garvey | Inspiration and Guidance |
| Mary McLeod Bethune | Inspiration and Guidance |
| Oscar De Priest | Role Model in Politics |
| Arthur W. Mitchell | Role Model in Politics |
| Black Newspapers (e.g., Chicago Defender, Pittsburgh Courier) | Information Dissemination and Advocacy |
White Reactions to the Great Migration
White responses to the Great Migration varied widely, reflecting the complex social and economic dynamics at play during this transformative period.
Some white politicians imposed migration fees, further burdening African American families seeking to escape the oppressive conditions of the South. This callous act added financial strain, exacerbating the already challenging journey to find better opportunities.
Additionally, the American Federation of Labor (AFL) actively excluded black workers from industrial jobs, limiting their access to economic advancement. This deliberate exclusion perpetuated economic disparity and hindered the ability of African Americans to improve their circumstances through gainful employment.
Impact on African American Pursuits
A significant impact on African American pursuits during the Great Migration was the pursuit of freedom and opportunities in new urban centers.
African American migration patterns shifted from rural to urban areas, leading to the formation of vibrant communities and the development of new social and political activism.
The influx of African Americans into northern and western cities brought about a surge in social and political engagement. This migration played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of American society, contributing to the emergence of influential African American leaders and organizations.
It also sparked a rich period of artistic expression and cultural renaissance, profoundly impacting black entertainment, global politics, and the desegregation of American sports.
The Great Migration epitomized the resilience and determination of African Americans in their pursuit of social and economic empowerment.
Formation of Community Institutions
The formation of community institutions during the Great Migration played a crucial role in fostering social and political engagement among African Americans in northern and western cities. This pivotal development evoked a sense of resilience and unity within the community, as they sought to establish a support network and advocate for their rights in unfamiliar territories.
The impact of these institutions can be emotionally evocative in the following ways:
- Empowerment: Building community centers and organizations provided a sense of empowerment and belonging, instilling hope and determination among African Americans.
- *Example*: The establishment of churches and social clubs served as pillars of strength and solidarity, offering a safe space for cultural preservation and mutual support.
- Resilience: These institutions symbolized the resilience of a marginalized community striving to create a better future despite facing adversity and discrimination.
- *Example*: Educational initiatives and mentorship programs demonstrated a commitment to overcoming societal barriers, inspiring a collective drive for progress and equality.
Rich Period of Artistic Expression
During the Great Migration, African American artistic expression flourished, reflecting the cultural vitality and resilience cultivated within the community institutions established in northern and western cities. This period marked the peak of the Harlem Renaissance, a significant African American cultural movement. The table below showcases the diverse range of artistic achievements during this era, demonstrating the profound impact of the migration on the cultural landscape.
| Artistic Expression | Notable Figures |
|---|---|
| Literature | Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston |
| Music | Louis Armstrong, Duke Ellington |
| Visual Arts | Jacob Lawrence, Augusta Savage |
| Performing Arts | Paul Robeson, Josephine Baker |
| Intellectual Discourse | W.E.B. Du Bois, Alain Locke |
The Harlem Renaissance not only gave birth to remarkable works of art but also catalyzed a broader societal recognition of African American cultural contributions, transcending geographical boundaries and shaping global perspectives on race, identity, and creativity.
Contributions of Black Alabamans
Black Alabamans played a significant role in shaping the cultural and political landscape during the Great Migration. Their contributions were profound and had a lasting impact on American society.
The cultural impact of Black Alabamans during the Great Migration can be evoked as follows:
- Prolific Artistic Expression: Black Alabamans contributed significantly to the New Negro Renaissance, showcasing their artistic talents and creativity. Their music, literature, and visual arts provided a powerful platform for expressing the struggles and triumphs of African American experiences, resonating with audiences across the nation.
- Political Activism: Black Alabamans were instrumental in advocating for civil rights and social justice, fostering a spirit of resilience and determination in the face of adversity.
These contributions not only enriched the cultural fabric of America but also laid the groundwork for future social and political movements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Were There Any Specific Laws or Regulations in Alabama That Directly Contributed to the Mass Exodus of African Americans During the Great Migration?
The specific laws and regulations in Alabama, such as legal segregation and discrimination, limited economic opportunities, and curtailed political activism, directly contributed to the mass exodus of African Americans during the Great Migration, impacting community institutions and cultural influence.
How Did the Great Migration Impact the Social and Cultural Landscape of Alabama, Specifically in Terms of Community Institutions and Political Activism?
The Great Migration profoundly impacted Alabama's social and cultural landscape, fostering community resilience and political mobilization. African Americans forged community institutions, cultivated political activism, and shaped a robust cultural legacy, epitomizing the enduring impact of this historic movement.
What Were Some of the Unique Challenges That African Americans From Alabama Faced When Migrating to the North and West, Compared to Those From Other Southern States?
African Americans from Alabama faced unique challenges when migrating to the North and West, including economic disparities, lack of community support, and distinct cultural impact. These challenges influenced their experiences in seeking opportunities and freedom.
What Role Did the Alabama-Based Black Newspapers, Such as the Birmingham World or the Mobile Beacon, Play in Encouraging or Facilitating the Great Migration?
Black newspapers in Alabama played a pivotal role in the Great Migration by providing a platform for community support, empowering African Americans, and addressing migration challenges. Their influential role in shaping public opinion encouraged and facilitated the migration.
Can You Provide Examples of Specific Contributions Made by Black Alabamans to the New Negro Renaissance, and How These Contributions Differed From Those of African Americans From Other Regions?
The specific contributions made by Black Alabamans to the New Negro Renaissance included influential literary works, music, and political activism. These contributions differed from those of African Americans from other regions due to unique challenges faced during the Great Migration and Alabama's impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Great Migration from Alabama had far-reaching effects on American society, sparking a period of cultural and artistic renaissance.
The mass exodus was driven by a combination of economic, social, and political factors, leading to the emergence of influential African American leaders and organizations.
The impact of the migration on African American pursuits and the formation of community institutions were significant, shaping the course of history in the United States.
Our Reader’s Queries
What factors pushed people from Alabama and pulled them to the north?
The majority of these migrants hailed from the Deep South, including states like Mississippi, Alabama, Arkansas, and Louisiana, where living conditions were especially tough. Floods, boll weevil infestations on cotton crops, lynchings, and segregation were some of the reasons that prompted them to seek a new home.
What was the largest migration in American history?
The Great Migration stands as one of the most massive population shifts in U.S. history. Over six million Black individuals relocated from the Southern to Northern, Midwestern, and Western regions between the 1910s and 1970s.
What was the Great Migration of the 1920s?
During the 1920s, over 750,000 African Americans departed from the South, marking a significant migration akin to that of the Irish potato famine in the 1840s. This mass exodus toward the Northeast and West sparked various transformations, as countless individuals from predominantly rural areas adapted to urban living for the first time.
What was the Great Migration to the Mississippi Territory?
From 1798 to 1819, the Great Migration kicked off in two major waves. The first wave started with the organization of the Territory and slowed down during the War of 1812. The second wave came in full force after the war ended in 1814.
Check Out For More References