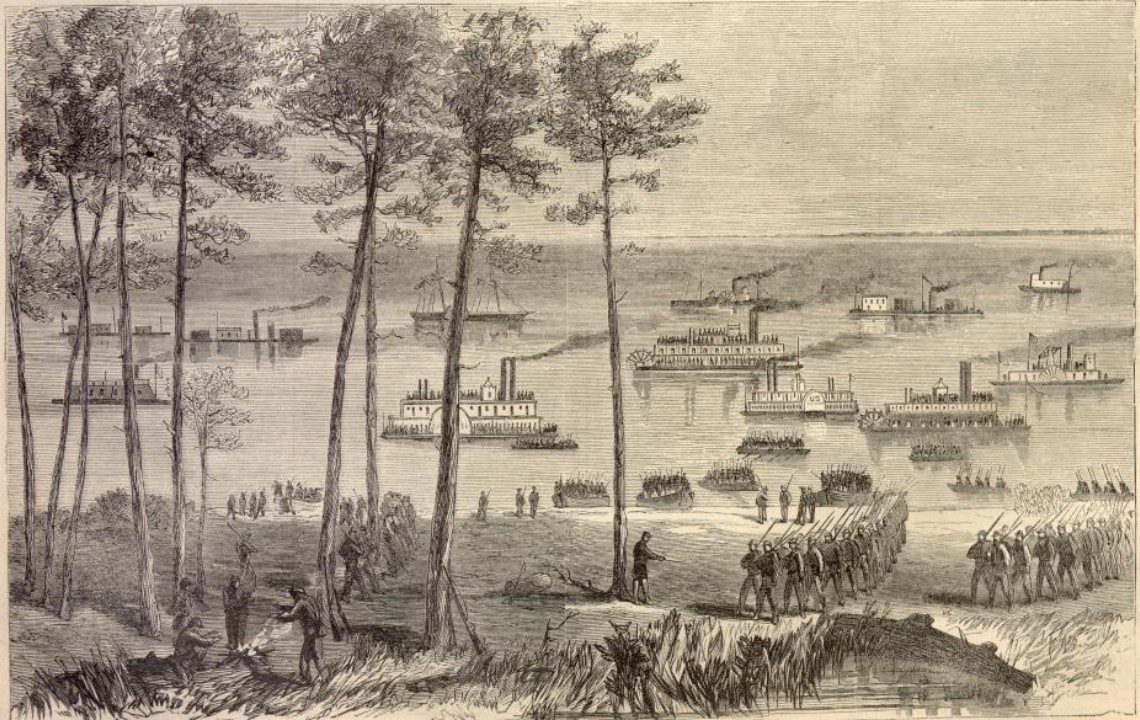The explosive showdown at Spanish Fort during the Civil War stands as a significant moment in the conflict's final stages.
Strategically positioned on the eastern approaches to Mobile, the Confederate fortifications at Spanish Fort played a pivotal role in the city's defense.
As Union forces launched a relentless assault, the subsequent battle showcased the tenacity of the Confederate defenders and the strategic acumen of the Union army.
The capture of Spanish Fort on April 8, 1865, not only led to the surrender of Mobile but also underscored the importance of this engagement in shaping the war's outcome.
This article delves into the background, defenses, federal advance, capture, surrender, and aftermath of the explosive showdown at Spanish Fort, shedding light on its enduring impact on Civil War history.
Key Takeaways
- Spanish Fort was a Confederate fortification guarding the eastern approaches to Mobile during the Civil War.
- The fort was captured by federal forces on April 8, 1865, leading to the surrender of the city of Mobile.
- The Confederate defenses of Spanish Fort included trenches, artillery redoubts, and underwater obstructions.
- The capture of Spanish Fort by federal forces resulted in the capture of about 500 prisoners and large quantities of artillery shells and gunpowder.
Spanish Fort: Confederate Defense Strategy
During the Civil War, Spanish Fort played a crucial role in the Confederate defense strategy guarding the eastern approaches to Mobile. The fortifications at Spanish Fort were an integral part of the Confederate defense plan, with Danville Ledbetter overseeing their construction to protect the eastern approaches.
The defenses at Spanish Fort included trenches, artillery redoubts, and underwater obstructions, strategically positioned to impede any Union advancement. Additionally, the fort was situated on a high hill with steep sides, providing a 360-degree view of the surrounding terrain, enhancing its defensive capabilities.
The Confederate forces, comprising six Louisiana infantry regiments, five Alabama infantry regiments, and 47 pieces of artillery, were strategically positioned to repel any Federal advance. Despite the eventual capture of Spanish Fort, the Confederate defense strategy played a significant role in delaying the Union forces and protecting Mobile for an extended period.
Federal Advance and Trench Warfare
The Confederate defenses at Spanish Fort faced a significant challenge as federal forces began massing in early January, prompting a strategic shift to trench warfare.
The federal forces, employing thousands of soldiers, initiated trench digging parallel to the Confederate line to close the distance while protecting their troops. Despite regular harassment by Confederate sharpshooters and artillery, the federal sappers persisted, engaging in intense artillery exchanges to protect the diggers.
In response, the Confederate resistance intensified, with their sharpshooters and artillery regularly targeting the federal sappers. This trench warfare strategy led to a prolonged and arduous battle, ultimately culminating in the capture of Spanish Fort on April 8.
The federal advance, combined with trench warfare tactics, played a pivotal role in the eventual success of the Union forces in the Battle of Spanish Fort.
Intense Artillery Exchanges
The relentless artillery exchanges between Confederate and federal forces marked a critical phase in the Battle of Spanish Fort, showcasing the fierce determination on both sides to gain tactical advantage.
- Artillery tactics played a pivotal role in shaping the outcome of the battle, as both sides strategically positioned and maneuvered their artillery pieces to target enemy positions.
- The impact on surrounding communities was profound, with the continuous sound of artillery fire creating a sense of unease and fear among the local residents.
- The artillery exchanges resulted in significant destruction of the landscape, with the surrounding areas bearing the scars of intense bombardment long after the battle had concluded.
- The psychological toll on civilians living in proximity to the battlefield was substantial, as the constant threat of artillery fire affected their daily lives and sense of security.
Breakthrough: Capture of Spanish Fort
The capture of Spanish Fort was a pivotal moment in the Battle of Spanish Fort, underscoring the strategic significance of the relentless artillery exchanges between Confederate and federal forces.
The significance of the breakthrough lies in the meticulous defense tactics at Spanish Fort, which included formidable fortifications such as trenches, artillery redoubts, and underwater obstructions.
Despite the challenging terrain and the determined Confederate defense, the federal forces successfully established defensive positions and strategically broke into the weak northern part of the battlefield, leading to the fort's capture.
This breakthrough marked the turning point in the battle, resulting in the evacuation of the fort by Confederate General Gibson and the surrender of about 500 prisoners and substantial quantities of artillery shells and gunpowder.
The meticulous and persistent federal tactics ultimately led to the capture of Spanish Fort and the subsequent surrender of Mobile.
Evacuation and Surrender of Spanish Fort
Following the pivotal capture of Spanish Fort, the evacuation and subsequent surrender marked the culmination of the relentless federal advance and the ultimate defeat of the Confederate forces.
Evacuation Strategy:
- Confederate General Gibson realized the inability to withstand continued federal attacks, leading to the evacuation of the fort.
- The Confederates spiked their guns, destroyed the gun carriages, and withdrew to Fort Huger.
Confederate Surrender:
- General Maury evacuated the city of Mobile, leaving about 4,500 men behind.
- Mobile surrendered without resistance three days after General Robert E. Lee's surrender.
The evacuation strategy and subsequent surrender demonstrated the deteriorating situation of the Confederate forces and the decisive victory of the federal advance.
Mobile's Surrender and Aftermath
After the capture of Spanish Fort, Mobile surrendered without resistance on April 12, 1865, marking a significant event in the Civil War's final days. The surrender of Mobile had a profound impact on the local economy and historical preservation efforts. It also contributed to the city's potential for tourism due to its rich Civil War history. The table below illustrates the impact on the local economy and the potential for tourism and historical preservation efforts.
| Impact on Local Economy | Tourism and Historical Preservation |
|---|---|
| Significant disruption due to war's end | Increased interest in Civil War history |
| Transition from wartime to peacetime economy | Preservation of Confederate and Union sites |
| Economic recovery and rebuilding | Potential for heritage tourism |
| Reintegration of soldiers into the workforce | Educational opportunities for visitors |
This pivotal moment in history has contributed to the ongoing narrative of the Civil War and its impact on the region's economic and cultural development.
Impact on Civil War History
Having withstood federal forces until April 8, 1865, the capture of Spanish Fort marked a significant turning point in Civil War history. The impact of Spanish Fort's capture on the outcome of the Civil War was profound. This pivotal event led to the surrender of the city of Mobile, effectively cutting off a crucial supply route for the Confederate forces and hastening the end of the war.
Additionally, the role of the Iron Bowl in promoting community unity and pride cannot be underestimated. This annual meeting of Auburn University's Tigers and the University of Alabama's Crimson Tide serves to showcase the passion and loyalty of the fans, attracting a large number of spectators and media attention while generating substantial revenue for both universities and the surrounding communities.
Preservation of Spanish Fort Battlefield
The preservation of the Spanish Fort battlefield remains a critical endeavor in commemorating its historical significance.
Preservation efforts have focused on protecting and maintaining the remaining earthworks and fortifications that played a crucial role in the Civil War.
Archaeological findings have provided valuable insights into the layout and construction of the fort, aiding in the accurate restoration and preservation of the site.
The state of Alabama has erected historical markers at several points on the battlefield, ensuring that the significance of Spanish Fort is recognized and understood.
Despite the encroachment of housing developments, ongoing efforts are dedicated to preserving the integrity of the battlefield and its historical importance.
It is imperative to continue these preservation endeavors to honor the sacrifices and events that unfolded at Spanish Fort during the Civil War.
Historical Markers and Commemoration
Seven historical markers have been erected by the state of Alabama at various points on the Spanish Fort battlefield to commemorate its historical significance. These markers serve as tangible symbols of the preservation efforts and community involvement in honoring the Civil War history of the area.
They provide detailed information about the events that transpired during the Battle of Spanish Fort and the significance of the site in the larger context of the war. The historical markers also contribute to the tourism opportunities in the region, attracting visitors interested in exploring and understanding this pivotal period in American history.
The commemoration through historical markers not only educates the public but also ensures that the sacrifices made and the impact of the battle are appropriately recognized and remembered.
Economic Impact: Iron Bowl and Community
The significance of the Battle of Spanish Fort extends to the economic impact of the region, notably exemplified by the highly anticipated annual event known as the Iron Bowl.
The Iron Bowl, an annual meeting of Auburn University's Tigers and the University of Alabama's Crimson Tide, is considered one of the most significant college football rivalries. This event attracts a large number of spectators and media attention, generating substantial revenue for both universities and the surrounding communities.
The influx of fans and media contributes to increased tourism, hotel bookings, and local business sales. The Iron Bowl showcases the passion and loyalty of the fans while significantly boosting the local economy.
Therefore, it plays a vital role in enhancing the economic prosperity of the region, making it a crucial annual event with far-reaching community impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Were the Specific Tactics and Strategies Used by the Confederate Forces to Defend Spanish Fort?
The Confederate defense of Spanish Fort relied on trench warfare, utilizing artillery tactics to repel the federal advance. Sharpshooters and artillery were employed to harass the federal sappers, while successive trenches and gun emplacements were utilized for defense.
How Did the Federal Forces Manage to Dig Trenches and Advance Towards the Confederate Fortifications While Under Constant Harassment?
The Federal forces managed to dig trenches and advance towards the Confederate fortifications despite constant harassment through careful planning, positioning of artillery, and utilizing defensive strategies, which ultimately contributed to the Civil War outcome.
What Types of Artillery Were Used During the Intense Exchanges Between the Confederate and Federal Forces?
During the intense exchanges between Confederate and federal forces, various types of artillery were utilized, including mortars, howitzers, and rifled guns. Civil War tactics emphasized the strategic deployment of artillery to disrupt enemy positions and inflict maximum damage.
What Were the Immediate Consequences and Impact of the Capture of Spanish Fort by the Federal Forces?
The immediate consequences of Spanish Fort's capture by federal forces included the surrender of Mobile, leading to the impact on the region with the evacuation of the city and the subsequent economic influence on the surrounding communities.
How Did the Surrender of Spanish Fort and the Subsequent Events Contribute to the Overall Outcome of the Civil War?
The surrender of Spanish Fort and subsequent events showcased Confederate resilience and contributed significantly to the overall outcome of the Civil War. The impact of surrender was pivotal, marking a turning point in the war's trajectory.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the capture of Spanish Fort in the Civil War had a significant impact on the outcome of the conflict.
The historical significance of this pivotal moment is reflected in the preservation of the battlefield and the commemoration of the events that took place.
Additionally, the economic impact of the Iron Bowl, an annual college football rivalry, generates over $15 million in revenue for the participating universities and their communities, further highlighting the enduring impact of historic events on modern society.
Our Reader’s Queries
What happened in Spanish Fort Alabama?
The Battle of Spanish Fort occurred from March 27 to April 8, 1865, as Union Forces launched a land campaign to seize Mobile from the East.
Who won the Battle of Spanish Fort?
Canby’s troops met at Danley’s Ferry on March 27th, 1865 and quickly began their attack on Spanish Fort. The Union completely surrounded the fort by April 1st and took control of it on April 8th. Brig. General Randall Gibson led the Confederate forces, who were mostly captured during this decisive moment.
What is Spanish Fort AL known for?
Spanish Fort boasts a variety of top attractions, such as the esteemed Historic Blakeley State Park, Meaher State Park, the cutting-edge VRium Robotics & Virtual Reality Amusement Park, 5 Rivers – Alabama’s Delta Resource Center, and the lively Kangarooz Family Fun Center.
What was the major purpose of the Spanish Fort?
The fortress, situated in what was once called the Village of Mobile, was constructed to protect Mobile and Fort Charlotte. The Spanish had captured Fort Charlotte from the British in March 1780, and the British were still a potential threat from nearby Pensacola.
Check Out For More References